4. Guidelines
Guiding principles are principles anticipated to lead the way for decision-makers and implementers in the efforts, identified in the Strategy Paper, to be made. The guiding principles will be as follows while implementing the traffic safety strategy:
- What is right should be done but one should be prepared against mistakes.
- The fragility of the human body should be considered in the design of roads, environment, and vehicles.
- The road traffic system should be handled as a whole and all elements of it should be strengthened.
- Responsibility sharing should be increased in traffic safety.
- All works should be based on concrete evidence, be measurable and assessable.
- Traffic safety efforts should support the well-being and health of people and strengthen a habitable environment.
- Traffic safety should be a priority in all decision-making processes.

The availability of clear and understandable guiding principles in traffic safety decision-making mechanisms is of a leading nature.
2021-2030 Traffic Safety Strategy is fundamentally based on the Safe System Approach and guiding principles were established as part of this approach in the paper. The main purpose of determining these principles is to consider these principles in infrastructure planning and traffic safety management and follow it up as a guideline in efforts and procedures.
All principles are equally important and form a complementary set of rules.
1- WHAT IS RIGHT SHOULD BE DONE, BUT ONE SHOULD ALSO BE PREPARED AGAINST MISTAKES
All road users are expected to comply with the rules and display proper behaviours. However, it is a fact that some road users may have faulty behaviours, and others may display risk-taking behaviours. A large part of the traffic accidents with tragic results originate from road users consciously violating traffic rules and happen as a consequence of a split-second inattentiveness or wrong decision. According to studies where the reasons of traffic accidents are researched, one can see that a great majority of the traffic accidents happen as a result of the split-second faulty decision of a vehicle driver or motorcyclist It is also a fact to be accepted that experienced well-trained drivers may also occasionally make mistakes.
The traffic system needs to be established in a way to prevent loss of life and serious injuries due to human error.
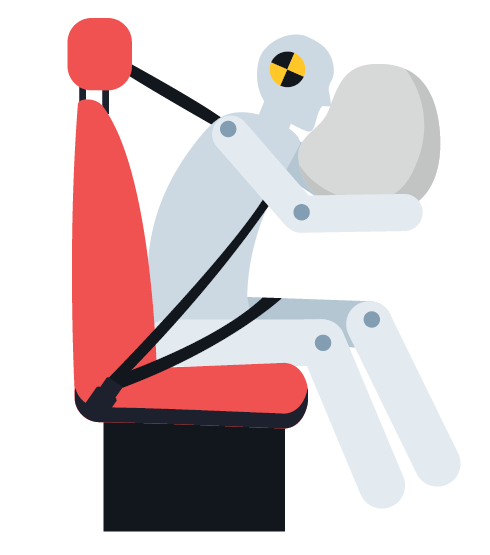
2-THE FRAGILITY OF HUMAN BODY SHOULD BE CONSIDERED IN THE DESIGN OF ROAD, ENVIRONMENT,
AND VEHICLE
The human body has a limit by which it can endure without getting harmed by the laws of physics. In case a traffic accident happens, the higher the force speed applied over the human is, the higher the possibility of death or injury becomes.
In case a vehicle faster than 30-40 km/hrs crashes into a pedestrian, cyclist, or motorcyclist, these persons get seriously injured or lose their lives. In case a car gets hit by another one from one side, if the speed of the crashing car is higher than 50 km/hrs, the persons in the crashed vehicle get seriously injured or lose their lives. In case two vehicles moving faster than 70-80 km/hrs collide one another head-on, the persons in both vehicles get seriously injured or lose their lives.
Some road user groups are more disadvantaged than other groups in traffic. Children, elderly people, and persons with disabilities display a more fragile structure than other road users. A serious increase is expected in the number of aforesaid vulnerable road users using the roads, due to the population in many countries getting gradually older, and for the transport modals such as walking, cycling, scooter, and motorcycles are preferred more.
Therefore, we should consider the endurance of human body against the severity of the collision, while constructing our roads, and take necessary measures to avert the results of human errors from causing deaths or serious injuries in traffic.
3- ROAD TRANSPORT SYSTEM SHOULD BE HANDLED AS A WHOLE AND ALL ELEMENTS OF IT SHOULD BE STRENGTHENED
The road transport system should be handled as a whole and all elements of it should be strengthened. Road and road perimeter, vehicles, speeding behaviour, and all risky user behaviours should be made safe in terms of traffic amongst the elements to be strengthened. The system should function to protect the human factor in case even one of these elements remains weak. As per the safe system approach, one should remember that the lack of strengthening of even one part of the system will impair the entire system. Furthermore, people getting harmed seriously can be prevented even in case of a traffic accident by increasing the safety levels of vehicles, designing the road infrastructure as “forgiving roads”, and with the proper and safe use of speed.
It is necessary to make the roads safer for all vulnerable road users especially the pedestrians, bicyclists, and motorcyclists regardless of being urban or upstate.
4- DIVISION OF RESPONSIBILITY SHOULD BE INCREASED IN TRAFFIC SAFETY
To ensure traffic safety balancedly and outrightly, it is necessary to divide the responsibility between the controllers, builders, and users of the traffic rules. Individuals, families, and the entire society play an important role in the making of traffic safety culture, the careful use of roads by showing necessary attention, and the protection of vulnerable road users.
Ensuring traffic safety shouldn’t be drape around road users with all its weight. The decision-makers at the institutions and organizations what we may call as system managers are to provide a safe road and road perimeter for the road users as part of their job.
One should also investigate how the loss of life or injury happened, analyse, and take measures to prevent its repetition, when there is a matter of loss of life or injury of a person at various levels, who didn’t comply with the traffic rules, depending on lack of information, prejudice, or physical/psychological inability.
Taking these measures, planning, construction and organization of roads; production, equipment, and placing on the market of vehicles both at central and local administrations level are matters to be handled balancedly by industry and manufacturing firms, and the ones responsible for the treatment and care of injured people including the post-accident emergency response.
Business and the industrial world have to provide a safe workplace environment for the people they employ, and the companies dealing with urban and intercity freight and passenger transport have to provide the necessary means to work in terms of occupational health and safety.
One of the fields where we focus our strategy is the institutions and organizations being traffic safety stakeholders to fulfil their responsibilities in a just, balanced, and proper manner.
5- ALL WORKS SHOULD BE BASED ON CONCRETE EVIDENCE, BE MEASURABLE, AND ASSESSABLE
Our efforts should be measurable and controllable to detect the problem areas awaiting solution. The traffic safety decision-making mechanisms should be supported with accurate, tangible, and controlled information to be attained from the field as well as the results of the efforts of science and academia to reach accurate decisions and generate proper solutions. Otherwise, labours and capitals will be invested in redundantly, and won’t serve the objective to prevent loss of life and property.
The detection and identification of new problems, arising with the traffic safety approach for collecting information, analysing and drawing a conclusion, will be possible with the necessary amendments to be made in the decennial period when the changes occurring in the traffic safety tendencies and the continuity of Strategy Paper.
It seems possible to ensure several technological advancements in the field of traffic safety in the next decade, besides, it is considered normal for the emergence of new problems in road traffic causing a dynamic environment. For these reasons, investing in research and development activities appears to be necessary to ensure the functioning of traffic safety without a hitch in the future.
Road and road perimeter, vehicle, road user, and post-accident intervention stages should be discussed in theses and researches in detail along with the efforts made in this approach, conclusions should be made, and put into practice with technological innovations. The results of efforts made by institutions separately should be provided to all parties, including local units and municipalities assigned in the field of traffic safety as needed, with a scientific perspective.
6- TRAFFIC SAFETY EFFORTS SHOULD SUPPORT THE WELL-BEING AND HEALTH OF PEOPLE AND STRENGTHEN A HABITABLE ENVIRONMENT
Intracity or upstate roads and avenues and streets aren’t merely a plot of grounds where vehicles move, they are structures which associate communities, cultures, economic activities, future, and hope with one another. Including the access way in front of our houses, the entire road network constitutes the indivisible part of social and economic life, where people come across and move for business and transactions. Due to such properties, our roads are also an integral part of public health and safety and a healthy and habitable environment
The urban roads, avenues, and streets, in particular, should be in a suitable and facilitator structure for persons with disabilities. The rights of persons with disabilities have been taken under protection with many national and international regulations, especially the “Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities”41 adopted with the Cabinet Decree Annex No. 2009/15137, one of which of these rights is the facilitation of the mobility of persons with disabilities.
A large part of the daily lives of people are spent on the roads in the hustling life-cycle of today, and travels may become more insufferable because of factors such as environmental pollution, emission, and excess noise. One should remember that it is an obligation to meet the expectations of the road users in the design of road and road perimeter.
7- TRAFFIC SAFETY EFFORTS SHOULD SUPPORT THE WELL-BEING AND HEALTH OF PEOPLE AND STRENGTHEN A HABITABLE ENVIRONMENT
Traffic safety must be considered as the priority in cases related to the social environment of people such as public health and sustainability, investment plans, and regulatory procedures.
While adopting this approach, it is necessary to avoid practices to avert the effective use of the road. Taking measures that complicate transport showing traffic safety as a reason constitutes a discrepancy against the spirit of this approach. Effectiveness and safety should be considered in coordination and equally in the use of the road network.

